What is Injection Molding Cost and How Does It Affect Manufacturing?
Injection molding is a vital process in the manufacturing industry. However, understanding injection molding cost can be challenging. Jason Millar, an industry expert, stated, “The true cost of injection molding extends beyond the mold itself.” This perspective highlights the complexities involved in assessing costs.
The injection molding cost includes materials, labor, and overhead. Manufacturers must consider these factors when budgeting projects. Even small changes in design can lead to significant cost variations. Attention to detail is crucial; a design flaw might inflate costs unexpectedly.
Moreover, companies often overlook maintenance expenses. Frequent mold repairs can add to production costs. Manufacturers need to reflect on their processes and strategies to optimize spending. Evaluating the injection molding cost can lead to better decisions in design and production. Understanding these financial elements is essential for success in today’s competitive market.

What is Injection Molding and Its Process Overview
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used for producing parts by injecting materials into a mold. Various materials, typically thermoplastics, are heated until they become liquid and then injected into a precisely designed mold. Once the material cools, it solidifies into the desired shape. This method can produce complex designs with high precision. The process is often favored for mass production due to its efficiency and reliability.
One aspect that can impact injection molding is the mold design. A poorly conceived mold can lead to defects in the final product. Additionally, the initial cost of creating a mold can be significant, sometimes deterring smaller manufacturers. Companies must balance quality and cost, often revisiting design elements. Choosing the right materials also plays a crucial role. Some materials require specific processing temperatures. Each of these factors adds complexity to the overall process. Despite the challenges, injection molding remains a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. The ability to create high-volume parts effectively is a defining feature of this technique.
Factors Affecting Injection Molding Costs in Manufacturing
Injection molding costs can vary significantly based on several key factors. Material selection plays a crucial role in determining expenses. Various plastics come with different price points. For example, high-performance polymers tend to be more costly than standard options. Consider the long-term performance requirements when making your choice, as this might impact costs over time.
The complexity of the mold also affects costs. A simple mold might be cheaper upfront, but it may not offer the best efficiency or quality. In contrast, a more complex mold can improve production speed and reduce defects. It requires a careful evaluation of your production needs. Sometimes, investing in a more complex mold pays off due to lower unit costs later.
**Tip**: Always get multiple quotes for tooling and materials. This helps in understanding the market better.
Labor costs cannot be overlooked, either. Skilled labor is often essential for effective molding operations. The location of your manufacturing facility also influences the overall expense. High-wage regions can significantly increase total cost.
**Tip**: Consider local labor markets when choosing a production site. It could save money in the long run.
Overall, each factor can lead to a different cost outcome. Evaluate each one carefully before proceeding with production.
Material Selection and Its Impact on Cost Efficiency
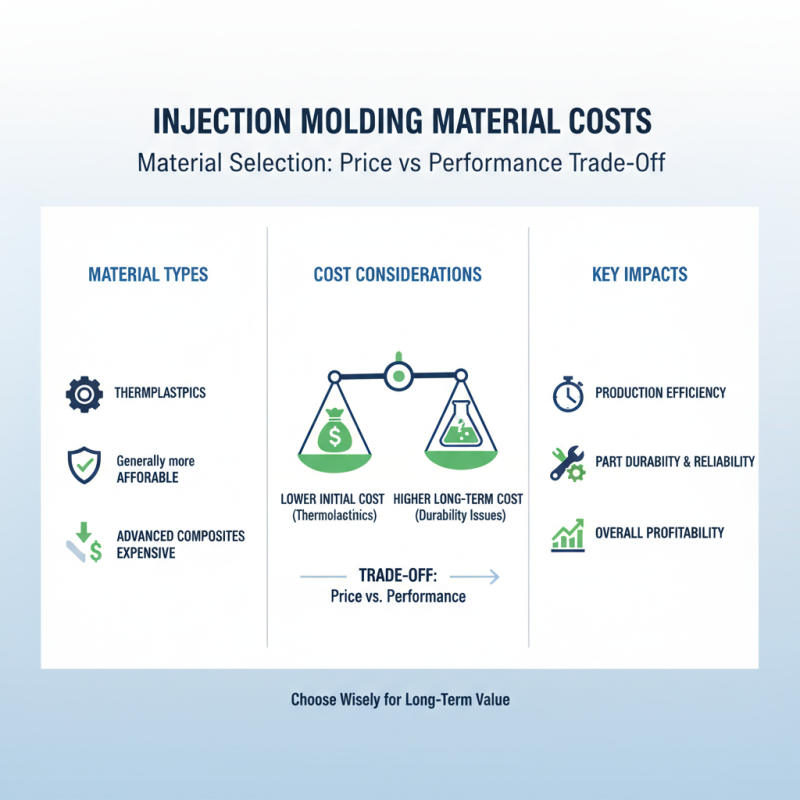
Material selection plays a crucial role in injection molding costs. Different materials come with varying price tags. For instance, thermoplastics are generally more affordable than advanced composites. Yet, performance often dictates the choice. Sometimes, a cheaper material may lead to issues later, like durability problems. This trade-off can increase costs over time.
The processing expenses can also fluctuate based on the chosen material. Some materials require specific temperatures and pressures. This adds to energy costs and equipment wear. Companies must evaluate their long-term needs and initial expenses carefully. Making the right choice can enhance cost efficiency. Alternatively, the wrong selection can lead to waste.
Designers often face tough decisions. They tackle factors such as weight, strength, and recycling. Balancing these elements affects the final costs, both in production and after-use. It’s essential to conduct thorough research. Sometimes, less expensive options seem appealing at first. However, they may not provide the best results. Reflecting on material choices is vital for sustainable success.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Injection Molding vs. Other Methods
Injection molding is a key technology in manufacturing, but how does its cost compare to other methods? A cost-benefit analysis reveals significant insights. According to recent industry reports, the average cost per part for injection molding can range from $0.001 to $0.50, depending on complexity, materials, and production volume. While initial setup costs are high, often exceeding $10,000, the per-unit costs decrease sharply with large-scale production.
For small to medium runs, other methods, like CNC machining, may appear cheaper initially. However, injection molding often becomes more cost-effective for larger volumes. Reports indicate that production runs of over 10,000 parts can save manufacturers up to 30% compared to CNC machining costs. Over time, the efficiency gains and cycle times in injection molding can lead to substantial savings.
**Tip:** Always analyze production volume before choosing a method. Low-volume production may benefit more from machines than injection.
Another consideration is material waste. Injection molding typically minimizes waste, making it an environmentally friendly choice. Traditional machining can result in significant excess material. Still, the upfront cost can deter some manufacturers. Finding the right balance requires thoughtful investment and consideration of future needs.
**Tip:** Consider material types and reusability when estimating costs. Some materials can reduce overall expenses despite their high upfront costs.
Long-term Financial Considerations of Injection Molding Operations
Injection molding is a process widely used for manufacturing plastic parts. However, it carries substantial long-term financial considerations. The initial setup costs for injection molds can be high, often requiring significant investment. This expense can impact cash flow, especially for startups or small businesses.
Operational costs also play a crucial role. Maintenance of machinery, energy consumption, and labor costs can add up over time. Inaccuracies in production can lead to waste, further straining budgets. It's vital to refine processes to minimize defects. Monitoring these factors carefully is essential for long-term profitability.
Companies should evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of injection molding. While the method can yield high volumes, slow production cycles can hinder efficiency. Analyzing every aspect of production helps in making financially sound decisions. Ultimately, understanding the economics of injection molding operations can lead to sustainable growth.